The SemaCyte® Microcarrier Platform
SemaCyte® cell assaying microcarriers leverage novel materials physics to move and freeze cells while retaining their adherent morphology. This approach introduces flexibility, speed, and miniaturisation into existing drug discovery workflows. We enhance standard cell assays to produce better data, faster.
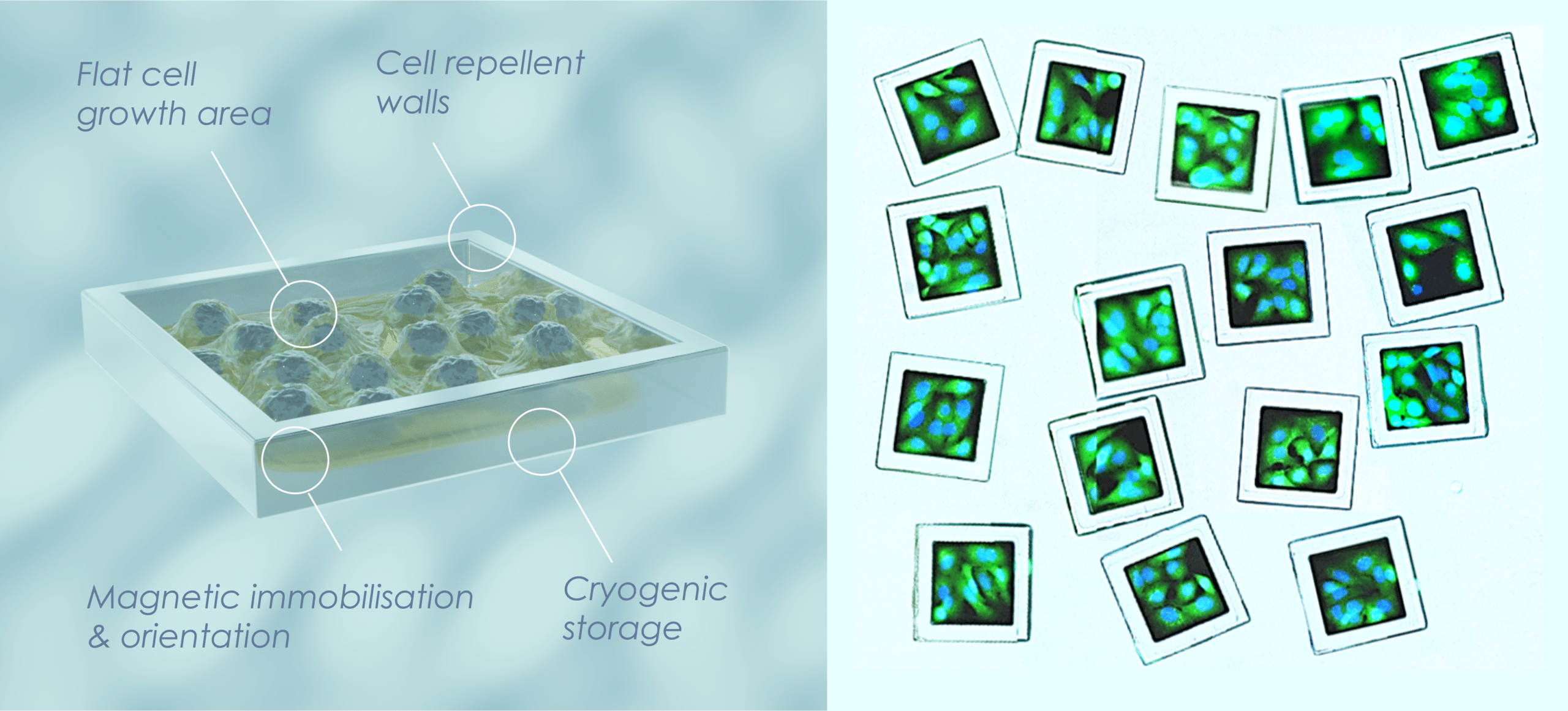
SemaCytes function as ultra-miniaturised, mobile wells which carry small colonies of adherent cells. These flat, walled cell microcarriers can be moved with liquid handling tools and their orientation can be controlled magnetically. SemaCytes can be used to measure additional experimental endpoints, prepare adherent assay-ready cells, and reduce the number of cells per well.
Enabling More Powerful Workflows with Cell Microcarriers
Move cells
while retaining their
adherent morphology
Increase assay flexibility and enable further workflow automation
e.g. subsample adherent cells to measure additional endpoints
Freeze adherent assay-ready cells in cryovials for on-demand use
Reduce assay preparation time to increase throughput by 2- to 20-fold
e.g. adherent assay-ready cells for rapid design-make-test-analyse cycles
Place less cells per well
while still retaining
high local confluency
Reduce the amount of adherent
cells per assay by 5- to 50-fold
e.g. ultra-miniaturise assays with primary cell materials in 96- or 384-well plates
Moving Adherent Cells to Enhance Assays
Ease-of-Use
Cells are simply seeded onto arrays of immobilized carriers on cell culture plasticware. After collection, these carriers can be cryopreserved or dispensed into microplates, streamlining assay workflows.
Broad Compatibility
SemaCyte microcarriers harmonize with various data analytics tools, assay types, read-out equipment, and lab automation tools, ensuring widespread adoption across life sciences.
For more information of the products, protocols, and experimental examples click here.
To watch our SemaCyte Microcarrier webinar to learn more click here.
SemaCytes are created with microfabrication technologies, combining nanomagnetism, smart materials, and surface engineering.
Cell seeding can be done as usual by simply pipetting cells on arrays of immobilised SemaCytes.
Once the correct confluency and morphology is achieved, the SemaCytes are released into suspension for direct use or cryopreservation.
Cell-containing SemaCytes are dispensed into a well plate for screening assays involving plate readers or microscopes.
